JEP 431: Sequenced Collections
Summary
Introduce new interfaces to represent collections with a defined encounter order. Each such collection has a well-defined first element, second element, and so forth, up to the last element. It also provides uniform APIs for accessing its first and last elements, and for processing its elements in reverse order.
"Life can only be understood backwards; but it must be lived forwards."
— Kierkegaard
Motivation
Java’s collections framework lacks a collection type that represents a sequence of elements with a defined encounter order. It also lacks a uniform set of operations that apply across such collections. These gaps have been a repeated source of problems and complaints.
For example, List and Deque both define an encounter order but their common supertype is Collection, which does not. Similarly, Set does not define an encounter order, and subtypes such as HashSet do not define one, but subtypes such as SortedSet and LinkedHashSet do. Support for encounter order is thus spread across the type hierarchy, making it difficult to express certain useful concepts in APIs. Neither Collection nor List can describe a parameter or return value that has an encounter order. Collection is too general, relegating such constraints to the prose specification, possibly leading to hard-to-debug errors. List is too specific, excluding SortedSet and LinkedHashSet.
A related problem is that view collections are often forced to downgrade to weaker semantics. Wrapping a LinkedHashSet with Collections::unmodifiableSet yields a Set, discarding the information about encounter order.
Without interfaces to define them, operations related to encounter order are either inconsistent or missing. While many implementations support getting the first or last element, each collection defines its own way, and some are not obvious or are missing entirely:
First element
Last element
**List**
list.get(0)
list.get(list.size() - 1)
**Deque**
deque.getFirst()
deque.getLast()
**SortedSet**
sortedSet.first()
sortedSet.last()
**LinkedHashSet**
linkedHashSet.iterator().next()
// missing
Some of these are unnecessarily cumbersome, such as getting the last element of a List. Some are not even possible without heroics: The only way to get the last element of a LinkedHashSet is to iterate the entire set.
Similarly, iterating the elements of a collection from first to last is straightforward and consistent, but iterating in reverse order is neither. All of these collections can be iterated forward with an Iterator, the enhanced for loop, a stream(), or toArray(). Iterating in reverse is different in every case. NavigableSet provides the descendingSet() view for reverse iteration:
for (var e : navSet.descendingSet())
process(e);
Deque does so with a reverse Iterator:
for (var it = deque.descendingIterator(); it.hasNext();) {
var e = it.next();
process(e);
}
List does so but with ListIterator:
for (var it = list.listIterator(list.size()); it.hasPrevious();) {
var e = it.previous();
process(e);
}
LinkedHashSet, finally, provides no support for reverse iteration. The only practical way to process the elements of a LinkedHashSet in reverse order is to copy its elements into another collection.
Similarly, processing a collection's elements using streams is a powerful and effective alternative to processing elements using loops, but obtaining a stream in reverse order can be difficult. Of the various collections that define encounter order, the only one that supports this conveniently is NavigableSet:
navSet.descendingSet().stream()
The others require either copying the elements to another collection or creating a stream from a customized Spliterator that reverses iteration.
This is an unfortunate state of affairs. The concept of a collection with defined encounter order exists in multiple places in the collections framework, but there is no single type that represents it. As a result, some operations on such collections are inconsistent or missing, and processing elements in reverse order ranges from inconvenient to impossible. We should fill these gaps.
Description
We define new interfaces for sequenced collections, sequenced sets, and sequenced maps, and then retrofit them into the existing collections type hierarchy. All of the new methods declared in these interfaces have default implementations.
Sequenced collections
A sequenced collection is a Collection whose elements have a defined encounter order. (The word "sequenced" as used here is the past participle of the verb to sequence, meaning "to arrange elements in a particular order.") A sequenced collection has first and last elements, and the elements between them have successors and predecessors. A sequenced collection supports common operations at either end, and it supports processing the elements from first to last and from last to first (i.e., forward and reverse).
interface SequencedCollection<E> extends Collection<E> {
// new method
SequencedCollection<E> reversed();
// methods promoted from Deque
void addFirst(E);
void addLast(E);
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
}
The new reversed() method provides a reverse-ordered view of the original collection. Any modifications to the original collection are visible in the view. If permitted, modifications to the view write through to the original collection.
The reverse-ordered view enables all the different sequenced types to process elements in both directions, using all the usual iteration mechanisms: Enhanced for loops, explicit iterator() loops, forEach(), stream(), parallelStream(), and toArray().
For example, obtaining a reverse-ordered stream from a LinkedHashSet was previously quite difficult; now it is simply
linkedHashSet.reversed().stream()
(The reversed() method is essentially a renamed NavigableSet::descendingSet, promoted to SequencedCollection.)
The following methods of SequencedCollection are promoted from Deque. They support adding, getting, and removing elements at both ends:
void addFirst(E)void addLast(E)E getFirst()E getLast()E removeFirst()E removeLast()
The add*(E) and remove*() methods are optional, primarily to support the case of unmodifiable collections. The get*() and remove*() methods throw NoSuchElementException if the collection is empty.
There are no definitions of equals() and hashCode() in SequencedCollection because its sub-interfaces have conflicting definitions.
Sequenced sets
A sequenced set is a Set that is a SequencedCollection that contains no duplicate elements.
interface SequencedSet<E> extends Set<E>, SequencedCollection<E> {
SequencedSet<E> reversed(); // covariant override
}
Collections such as SortedSet, which position elements by relative comparison, cannot support explicit-positioning operations such as the addFirst(E) and addLast(E) methods declared in the SequencedCollection superinterface. Thus, these methods can throw UnsupportedOperationException.
The addFirst(E) and addLast(E) methods of SequencedSet have special-case semantics for collections such as LinkedHashSet: If the element is already present in the set then it is moved to the appropriate position. This remedies a long-standing deficiency in LinkedHashSet, namely the inability to reposition elements.
Sequenced maps
A sequenced map is a Map whose entries have a defined encounter order.
interface SequencedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> {
// new methods
SequencedMap<K,V> reversed();
SequencedSet<K> sequencedKeySet();
SequencedCollection<V> sequencedValues();
SequencedSet<Entry<K,V>> sequencedEntrySet();
V putFirst(K, V);
V putLast(K, V);
// methods promoted from NavigableMap
Entry<K, V> firstEntry();
Entry<K, V> lastEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry();
}
The new put*(K, V) methods have special-case semantics, similar to the corresponding add*(E) methods of SequencedSet: For maps such as LinkedHashMap, they have the additional effect of repositioning the entry if it is already present in the map. For maps such as SortedMap, these methods throw UnsupportedOperationException.
The following methods of SequencedMap are promoted from NavigableMap. They support getting and removing entries at both ends:
Entry<K, V> firstEntry()Entry<K, V> lastEntry()Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry()Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry()
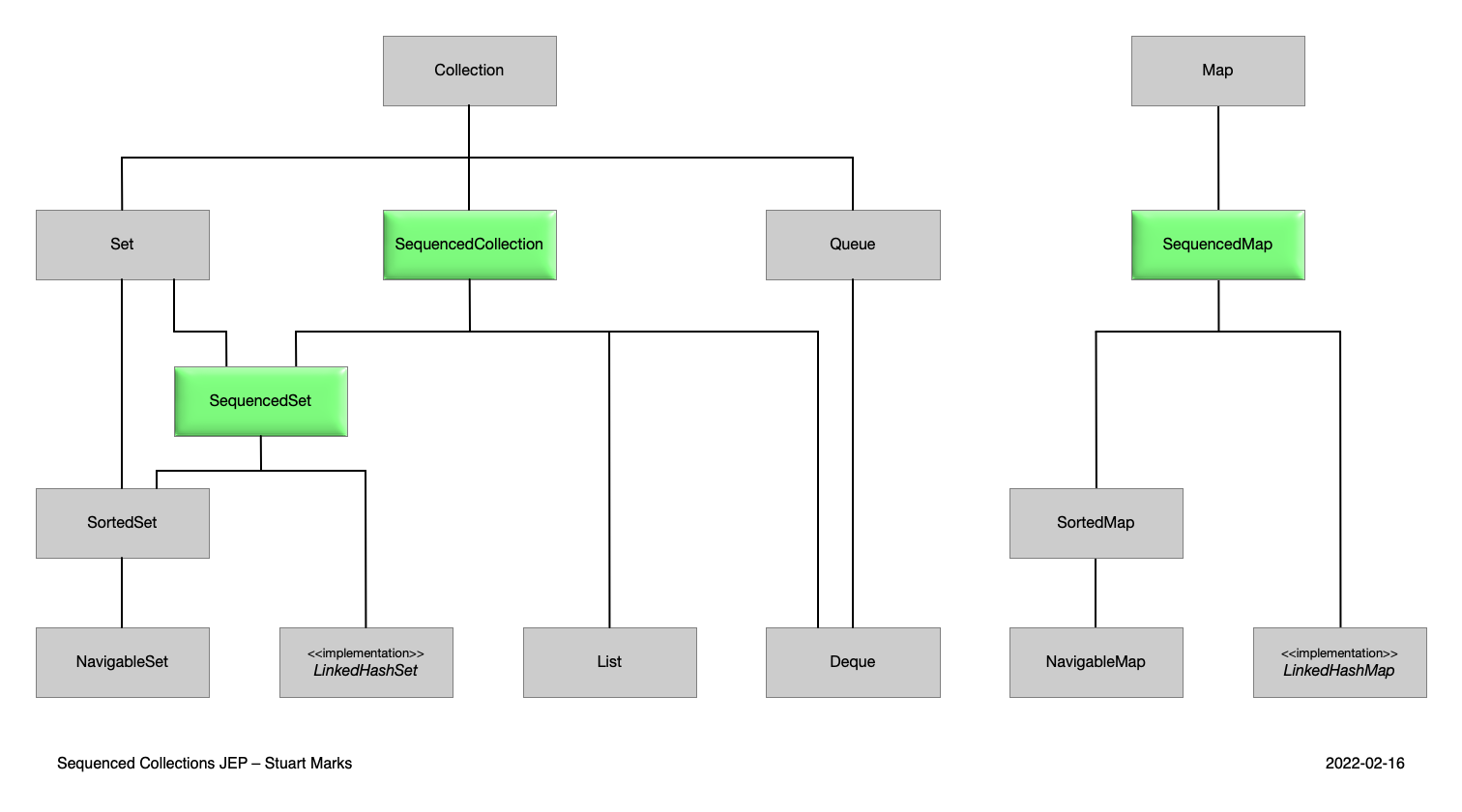
Retrofitting
The three new interfaces defined above fit neatly into the existing collections type hierarchy (click to enlarge):
In detail, we make the following adjustments to retrofit existing classes and interfaces:
Listnow hasSequencedCollectionas its immediate superinterface,Dequenow hasSequencedCollectionas its immediate superinterface,LinkedHashSetadditionally implementsSequencedSet,SortedSetnow hasSequencedSetas its immediate superinterface,LinkedHashMapadditionally implementsSequencedMap, andSortedMapnow hasSequencedMapas its immediate superinterface.
We define covariant overrides for the reversed() method in the appropriate places. For example, List::reversed is overridden to return a value of type List rather than a value of type SequencedCollection.
We also add new methods to the Collections utility class to create unmodifiable wrappers for the three new types:
Collections.unmodifiableSequencedCollection(sequencedCollection)Collections.unmodifiableSequencedSet(sequencedSet)Collections.unmodifiableSequencedMap(sequencedMap)
Alternatives
Types
An alternative to adding new types would be to repurpose the List interface as a general sequenced collection type. Indeed List is sequenced, but it also supports element access by integer index. Many sequenced data structures do not naturally support indexing and would thus be required to support it iteratively. This would result in indexed access having O(n) performance instead of the expected O(1), perpetuating the mistake of LinkedList.
Deque seems promising as a general sequence type, since it already supports the right set of operations. However, it is cluttered with other operations, including a family of null-returning operations (offer, peek, and poll), stack operations (push and pop), and operations inherited from Queue. These operations are sensible for a queue but less so for other collections. If Deque were repurposed as a general sequence type then List would also be a Queue and would support stack operations, resulting in a cluttered and confusing API.
Naming
The term sequence, which we have chosen here, implies elements that are arranged in order. It is commonly used across various platforms to represent collections with semantics similar to those described above.
The term ordered is not quite specific enough. We require iteration in both directions, and operations at both ends. An ordered collection such as a Queue is a notable outlier: It is ordered, but it is also decidedly asymmetric.
The term reversible, used in an earlier version of this proposal, does not immediately evoke the concept of having two ends. Perhaps a bigger issue is that the Map variant would be named ReversibleMap, which misleadingly implies that it supports lookup by key and by value (sometimes called a BiMap or BidiMap).
Add, put, and UnsupportedOperationException
As described above, explicit-positioning APIs such as SortedSet::addFirst and SortedMap::putLast throw UnsupportedOperationException because the sequence of their elements is determined by relative comparison. The asymmetry of having some collections not implement all of the SequencedCollection operations may seem unpleasant. It is nonetheless valuable because it brings SortedSet and SortedMap into the sequenced collection family, allowing them to be used more broadly than otherwise. This asymmetry is, also, consistent with prior design decisions in the collections framework. For example, the Map::keySet method returns a Set, even though the implementation returned does not support addition.
Alternatively, the addition operations could be kept separate by rearranging the interfaces along structural lines. That would result in new interface types with very thin semantics (e.g., AddableCollection) that are not useful in practice and that clutter up the type hierarchy.
History
This proposal is an incremental evolution of our 2021 ReversibleCollections proposal. The major changes from that proposal are renaming, the addition of the SequencedMap interface, and the addition of unmodifiable wrapper methods.
The ReversibleCollection proposal was in turn based on Tagir Valeev's 2020 OrderedMap/OrderedSet proposal. Several fundamental concepts from that proposal are still present, although there are many differences in detail.
Over the years we have received many requests and proposals in the vein of combining a List with a Set or Map. The recurring themes are a List that contains unique elements, or a Set or Map that maintains ordering. These requests include 4152834, 4245809, 4264420, 4268146, 6447049, and 8037382.
Some of these requests were partially addressed with the introduction of LinkedHashSet and LinkedHashMap in Java 1.4. While those classes do satisfy some use cases, their introduction left gaps in the abstractions and operations provided by the collections framework, as described above.
Testing
We will add a comprehensive set of tests to the JDK's regression test suite.
Risks and Assumptions
Introducing new methods high in the inheritance hierarchy runs the risk of clashes over obvious method names such as reversed() and getFirst().
Of particular concern are the covariant overrides of the reversed() method on List and Deque. These are source and binary incompatible with existing collections that implement both List and Deque. There are two examples of such collections in the JDK: LinkedList and an internal class sun.awt.util.IdentityLinkedList. The LinkedList class was handled by introducing a new reversed() covariant override on LinkedList itself. The internal IdentityLinkedList class was removed as it was no longer necessary.
An earlier version of the proposal introduced covariant overrides for the keySet(), values(), and entrySet() methods of the SequencedMap interface. After some analysis it was determined that this approach introduced too great a risk of incompatibilities; essentially, it invalidates any existing subclasses. An alternative approach was selected, which was to introduce new methods sequencedKeySet(), sequencedValues(), and sequencedEntrySet() into SequencedMap instead of adjusting the existing methods to be covariant overrides. In retrospect, it may have been for the same reason that a similar approach was taken in Java 6 with the introduction of the navigableKeySet() method instead of modifying the existing keySet() method to be a covariant override.
See the report attached to the CSR, JDK-8266572, for a full analysis of the incompatibility risk.